Cryptocurrencies have redefined how we perceive money, ownership, and decentralized systems. Since the launch of Bitcoin in 2009, the digital asset landscape has exploded, offering numerous use cases and opportunities.
Whether for business innovation, community building, or decentralized finance (DeFi), creating your own cryptocurrency is more accessible than ever—provided you understand the necessary technical and strategic foundations.
This comprehensive guide dives deep into the process of creating your own cryptocurrency, beginning with how cryptocurrencies work and moving step by step through the technical, legal, and promotional aspects of how to create your own cryptocurrency from scratch.
How Do Cryptocurrencies Work?
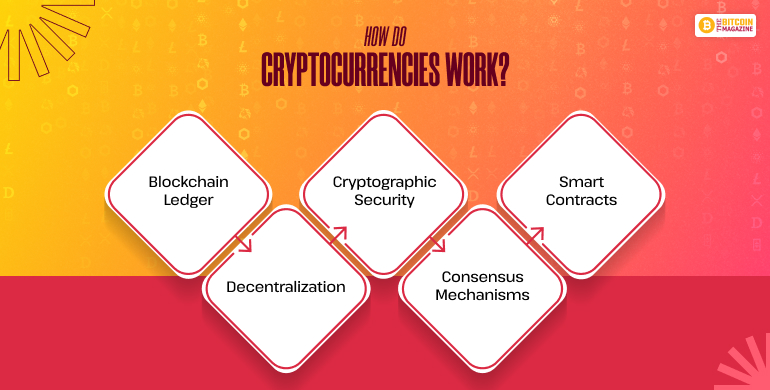
Cryptocurrency development on blockchain technology—a decentralized, immutable ledger that records all transactions across a network of computers (nodes). Key components include:
1. Blockchain Ledger
The blockchain is a continuously growing chain of blocks, each containing a record of multiple transactions. It ensures transparency and traceability.
2. Decentralization
Instead of a single central authority, a distributed network of nodes maintains the blockchain. Each node has a full or partial copy of the ledger.
3. Cryptographic Security
Transactions and wallet data are secured via public and private keys, using advanced cryptographic algorithms like SHA-256.
4. Consensus Mechanisms
Consensus algorithms ensure all nodes agree on the validity of transactions. Examples include Proof of Work (PoW), Proof of Stake (PoS), and others.
5. Smart Contracts
These are self-executing contracts with predefined conditions encoded in software. They automate processes and transactions without intermediaries.
How to Create Your Own Cryptocurrency from Scratch: Taking Uniswap (UNI) For Example
Uniswap is a decentralized exchange (DEX) that operates on the blockchain network, that enables the user into trading cryptocurrencies through an automated liquidity pool.
With the use of smart contracts, it facilitates the token swaps without any intermediaries, at the same time it supports the decentralized finance (DeFi) application.
What Are the Types of Cryptocurrencies?
Cryptocurrencies can be categorized based on their utility and the platforms they operate on:
1. Coins
Coins like Bitcoin and Litecoin operate on their own independent blockchains.
2. Tokens
Tokens are built on existing blockchains like Ethereum. Examples include ERC-20 tokens.
3. Stablecoins
Stablecoins are pegged to stable assets like fiat currencies (e.g., USDT, USDC) to reduce volatility.
4. Utility Tokens
These tokens provide access to a product or service within a blockchain ecosystem (e.g., Basic Attention Token).
5. Security Tokens
They represent ownership in real-world assets and are subject to regulatory oversight.
6. Governance Tokens
These allow token holders to vote on protocol decisions (e.g., Uniswap’s UNI token).
Why Do You Want to Make a Cryptocurrency?
Clarifying your intention behind creating a cryptocurrency is critical. Common motivations include:
- Developing a decentralized app (dApp)
- Launching a community coin
- Supporting a DeFi platform
- Enabling micropayments or loyalty systems
- Raising capital through token sales (ICOs/IDOs)
- Creating a private, internal payment solution
Your objective will guide the design, technology stack, legal structure, and promotional strategies.
How to Create Your Own Cryptocurrency from Scratch: Step-by-Step Guide

| Step | Description | Key Activities | Considerations |
| Define Purpose | Specify the core purpose and target audience of the cryptocurrency. | Determine the problem it solves or the market it serves. | Ensure the purchase aligns with demand in the marketplace and potential user group. |
| Choose a Consensus Mechanism | Select the appropriate mechanism for validating transaction | Make a decision between PoW, PoS, DPoS, PBFT, or hybrid. | Consider security, energy consumption, and scalability. |
| Select a Blockchain Platform | Choose the underlying technology of the cryptocurrency | Evaluate Ethereum, Binance, Smart Chain, Polkadot, etc. | Evaluate community support, compatibility, and technicalities. |
| Design the Nodes | Deploy and configure the network nodes that will support the blockchain. | Make decisions between Full nodes and Light nodes, centralized vs decentralized. | Highlight distribution, scalability, and security features. |
| Establish Internal Architecture | Set the technical configuration of the blockchain. | Set permissions, address formats, key management, data storage, and smart contracts. | Make secure and robust design to allow functionalities and compliance. |
| Integrate APIs | Execute APIs for wallets, exchanges, and payment gateways. | Execute APIs for wallets, exchange, and payment gateways. | Select APIs that are more secure, user-friendly, and flexible. |
| Design the Interface | Use proper programming languages and focus on UX design. | Use proper programming languages and focus on UX design. | Make the interface secure, intuitive, and user-friendly. |
| Ensure Legal Compliance | Follow international laws, and follow AML/KYC norms. | Follow international laws, local laws, and follow AML/KYC norms. | Ensure transparency and remain current with regulatory updates. |
| Promote the Cryptocurrency | Engage in online marketing, community, partnerships, and ICOs if needed. | Engage in online marketing, community building, partnerships, and ICOs if needed. | Build credibility, raise awareness, and encourage adoption. |
Step 1: Define Your Purpose
The first step of creating a cryptocurrency determines the purpose of creating your own cryptocurrencies.
- Target Audience
Identify your core users. Are they retail investors, enterprises, gamers, content creators, or others?
- Use Cases
Outline how the token will be used: payments, staking, governance, access rights, rewards, etc.
- Economic Model and Tokenomics
Develop your currency’s financial blueprint:
- Token supply: Fixed, inflationary, or deflationary?
- Initial distribution: ICO, airdrop, pre-mine?
- Utility: What will users do with the token?
- Incentives: Rewards for validators, users, and developers.
Step 2: Choose a Consensus Mechanism
The consensus mechanism secures your network. Options include:
- Proof of Work (PoW): High security, energy intensive.
- Proof of Stake (PoS): Energy-efficient, faster transaction times.
- Delegated PoS (DPoS): Uses a small set of trusted validators.
- Proof of Authority (PoA): Suitable for private blockchains.
- Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (PBFT): Enterprise-grade blockchains.
Step 3: Select a Blockchain Platform
You can:
- Develop a new blockchain: Full control, complex to build.
- Fork an existing blockchain: Clone an open-source protocol (e.g., Bitcoin, Ethereum).
- Use a blockchain platform: Deploy a token on Ethereum, BSC, Solana, Avalanche, or Polygon.
Factors to consider:
- Development complexity
- Community and developer support
- Transaction speed and fees
- Scalability and interoperability
Step 4: Design the Nodes
Nodes validate and propagate transactions. Decide on:
- Node types: Full vs. light nodes
- Access model: Public, private, or consortium
- Geographic distribution: Ensure network decentralization
Set up your own nodes or leverage third-party services like Infura or Alchemy.
Step 5: Establish Blockchain Architecture
Key architectural decisions include:
- Block size and block time
- Consensus rules and network parameters
- Smart contract capabilities
- Address format and transaction structure
- Upgradeability (hard forks or modular updates)
Use frameworks like Substrate (for Polkadot) or Cosmos SDK to streamline development.
Step 6: Integrate APIs
APIs are essential for interaction with the blockchain. Use:
- Crypto APIs: For real-time price, trading data, and transaction tracking.
- Wallet integration APIs: Metamask, Trust Wallet
- Payment APIs: Enable fiat-to-crypto gateways
- Explorer APIs: For transaction history and blockchain search
Step 7: Design the Interface
Build user-friendly interfaces for different users:
- Wallet UI: Enable sending, receiving, and staking
- Web dashboard: Token balances, analytics, governance votes
- Mobile app: For broader accessibility
- Admin panel: Monitor network performance, user activity
Focus on security, UX design, and responsiveness.
Step 8: Make Your Cryptocurrency Legal
Cryptocurrency regulations vary across jurisdictions. Steps include:
- Legal entity registration
- Complying with KYC/AML regulations
- Understanding securities law (especially for ICOs/IEOs)
- Drafting legal disclaimers, privacy policies, and user agreements
- Consulting with crypto-legal experts
Step 9: Promote Your Cryptocurrency
Marketing is crucial for adoption. Key strategies:
- Social Media: Twitter, Discord, Telegram, Reddit
- Content Marketing: Blogs, podcasts, YouTube
- Community Building: Host AMAs, giveaways, contests
- Exchange Listings: Apply to DEXs (like Uniswap) and CEXs
- Partnerships: Collaborate with other blockchain projects
- Incentive Programs: Airdrops, staking rewards, referral bonuses
What Common Mistakes You Need to Avoid While Making Cryptocurrency
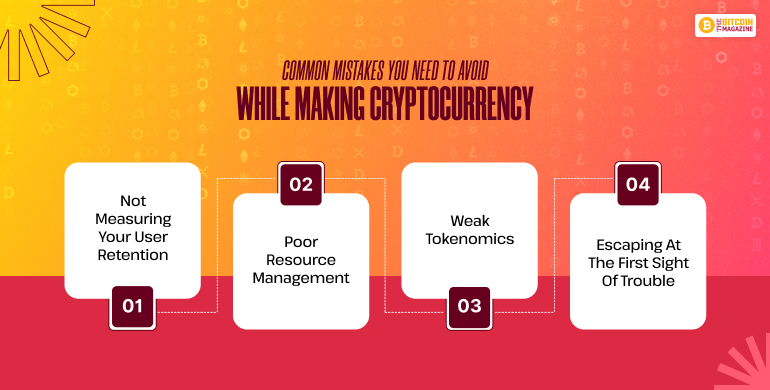
When you are building a cryptocurrency on your own it is obvious to face certain challenges on the way, since there are quite a lot of things that you need to keep in mind.
So few of the mistakes that you should avoid while creating your own cryptocurrency from scratch are as follows.
Not Measuring Your User Retention
Most crypto projects have a very strong user acquisition strategy and usually nullify retention mechanisms.
Until such a time when you know how many users are engaging and why the rest are falling, it will be difficult to build a loyal community or even work towards long-term sustainability.
Poor Resource Management
Misallocation of funds, overspending on employment, too much marketing investment without a robust product can result in early burnout.
Good budgeting and strategic planning are very needed for the current state of the volatile crypto landscape.
Weak Tokenomics
Without a clear effective use case, an inflationary approach, as well as proper distribution for your token, it may disappoint investors and users.
Such strong tokenomics makes placement for value and purpose behind your coin or token, which is the very backbone of a successful crypto project.
Escaping at the First Sight of Trouble
The crypto space is very fickle in nature. Projects draining at the first sign of a downturn have to be considered appropriately.
It’s a resilient team that adopts communicative transparency and keeps building while facing bad times earns trust and longevity through time.
How to Create Your Own Cryptocurrency from Scratch: Pros and Cons

Before you determine how to create your own cryptocurrency from scratch, it is important to assess the pros and cons of creating your own crypto.
Pros
- Full control over monetary policy
- Innovative business models
- Direct community engagement
- Potential for exponential growth
- Decentralized value creation
Cons
- Technical complexity
- Security risks (hacks, bugs)
- Regulatory uncertainty
- Market saturation
- Adoption challenges
Do You Have the Technical Knowledge to Program and Maintain Cryptocurrency?
Before diving in, assess your technical expertise. Key skills include:
- Blockchain development (languages: Solidity, Rust, Go, JavaScript)
- Smart contract creation and auditing
- Understanding consensus algorithms
- Node and network deployment
- Managing crypto wallets and APIs
- Knowledge of cryptographic principles and token standards
If you’re not well-versed in these areas, consider hiring a development team or partnering with a blockchain consultancy.

