Ethereum is not simply a cryptocurrency — it’s the foundation for a whole decentralized economy powering smart contracts, DeFi, NFTs, DAOs, and so much more.
Ethereum began small and has evolved to revolutionize the form of blockchain and with it, much more than peer-to-peer value-based transactions.
In this article I am going to break down the history of Ethereum, how Ethereum works, and where Ethereum is headed — telling us the entire story of one of the greatest platforms in crypto history.
What Is Ethereum?
Ethereum is an open-source decentralized blockchain platform that empowers application developers to create and publish smart contracts — self-executing computer programs with programmed actions as specified and with no scope for fraud or censorship.
The native cryptocurrency of Ethereum is Ether (ETH) and is used to reward calculations and transactions on the network.
Bitcoin stands apart in that it essentially only exists as a vehicle to be exchanged within peer-to-peer electronic trading. Ethereum’s power lies in the potential of it being a programmable blockchain.
History of Ethereum
Vitalik Buterin, the co-founder of Ethereum once said “I thought (those in the Bitcoin community) weren’t approaching the problem in the right way. I thought they were going after individual applications; they were trying to kind of explicitly support each (use case) in a sort of Swiss Army knife protocol.”
That is when he thought of a different way of thinking.
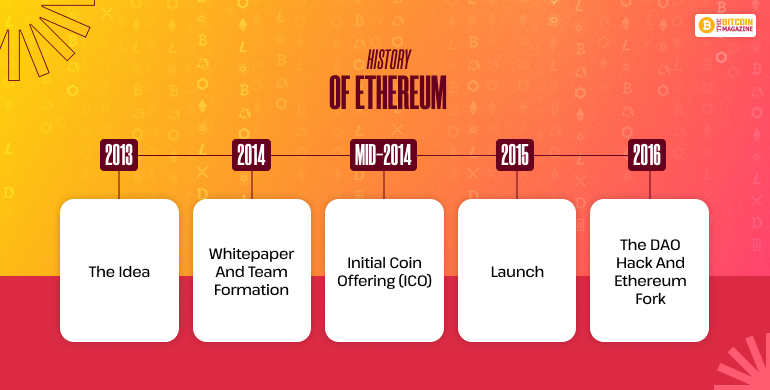
1. The Idea (2013)
Ethereum was founded in late 2013 by Vitalik Buterin, a Russian-Canadian developer who had developed Bitcoin but was limited by its scripting language.
He wanted to establish a new platform on the foundation of a Turing-complete programming language, which could run more advanced applications than payments alone.
2. Whitepaper and Team Formation (2014)
The Ethereum whitepaper was authored and published by Buterin in 2014 for a world computer vision for a decentralized one. Key co-founders were:
- Vitalik Buterin
- Gavin Wood (went on to develop the Solidity, Ethereum’s programming language)
- Joseph Lubin (went on to create ConsenSys)
- Charles Hoskinson (went on to create Cardano)
- Anthony Di Iorio and Mihai Alisie
3. Initial Coin Offering (ICO)
To finance its development, Ethereum organized one of the very first large-scale ICOs in mid-2014, collecting more than $18 million of Bitcoin, a at-the-time record-breaking amount.
4. Launch (2015)
Ethereum launched its first version, named Frontier, on July 30, 2015. It was the launch of Ethereum as a live public blockchain.
5. The DAO Hack and Ethereum Fork (2016)
In 2016, a project, The DAO, collected $150 million in ETH. Hackers broke the bug in the code and stole approximately $50 million. To recover the money, to do so, the Ethereum community hard-forked the chain:
- Ethereum (ETH): The chain was recovered which replaced the hack.
- Ethereum Classic (ETC): The original chain which maintained the hack.
This was an historic moment in the history of Ethereum and revealed the strength of governance and community in determining blockchain networks.
How Does Ethereum Work?

Ethereum works by allowing users to write smart contracts — chunks of code immutably stored on the Ethereum blockchain that run independently when certain conditions are met.
Contracts are enforced automatically and cannot be altered, which allows for an array of decentralized applications (dApps).
Key Features:
- Smart Contracts
- Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM): Distributed computer upon which all Ethereum apps run.
- Ether (ETH): To fuel applications and conduct transactions.
Blockchain Technology
Essentially, Ethereum is built on a blockchain, distributed ledger technology, where every transaction is stored in a safe, chronological record.
Every node (computer) in the Ethereum network maintains an exact copy of the blockchain and work together to validate new transactions, thus enabling decentralization and security.
PoS Validation Process
Originally based on Proof-of-Work (PoW) like Bitcoin, Ethereum converted to Proof-of-Stake (PoS) since September 2022 with “The Merge”.
Key PoS Features:
- Stakers (validators) lock up ETH in order to create and validate blocks.
- Less power-hungry compared to PoW.
- Greater scalability capacity.
- Increased security and decentralization incentives.
This transition already reduced Ethereum’s energy consumption by over 99.95%, a historic milestone for blockchain sustainability.
Wallets
They will need a wallet to be able to use Ethereum. They come in all sorts of formats:
Types of Ethereum Wallets:

- Hot Wallets: Internet-connected (e.g., MetaMask, Trust Wallet).
- Cold Wallets: Storage off-line for greater security (e.g., Ledger, Trezor).
- Web Wallets: Accessed through web browsers (e.g., MyEtherWallet).
- Mobile Wallets: Phone apps.
- Desktop Wallets: Installed on computers (e.g., Exodus).
Wallets store private keys and allow people to send, receive, and interact with smart contracts.
What is the Difference Between Ethereum and Bitcoin?

On one hand there are quite a few similarities between Bitcoin and Ethereum, but on the other hand there are many differences between the two as well. So, let’s check out a few differences between Ethereum and Bitcoin.
- Firstly, Bitcoin primarily trades in Cryptocurrency, whereas Ethereum trades on several methods of exchange, that includes Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM), Cryptocurrency (Called Ether), and Smart Contracts.
- Secondly, both have different security protocols in place: Ethereum has – “proof of stake” and Bitcoin has – “proof of work” systems.
- Bitcoin only allows public transactions to take place (permissioned or censor-proof); while Ethereum allows both permissionless and permissioned transactions.
- The average block time between Ethereum and Bitcoin is quite different. While Bitcoin takes 10 minutes to block confirmations, Ethereum takes only 12 seconds, which helps miners to complete more blocking and receiving Ether’s faster.
What Are the Benefits of Ethereum?
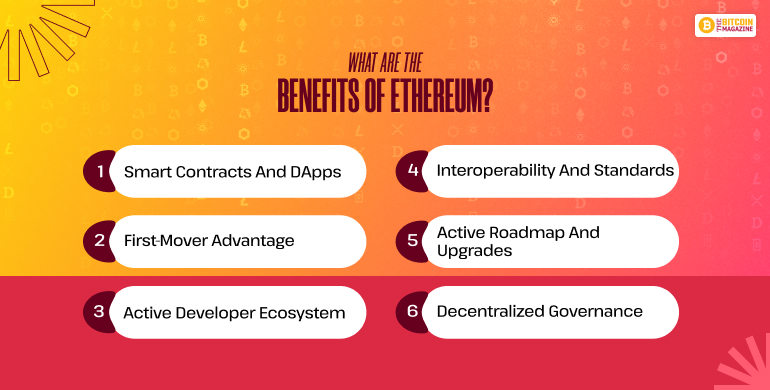
- Smart Contracts and dApps: Enabling decentralized, trustless operation in a global context.
- First-Mover Advantage: Biggest DeFi, NFT, etc. ecosystem.
- Active Developer Ecosystem
- Interoperability and Standards: (e.g., ERC-20, ERC-721)
- Active Roadmap and Upgrades
- Decentralized Governance
The Future of Ethereum
Ethereum continues growing at the rapid rate, with a distinct development road map to decentralization, security, and scalability.
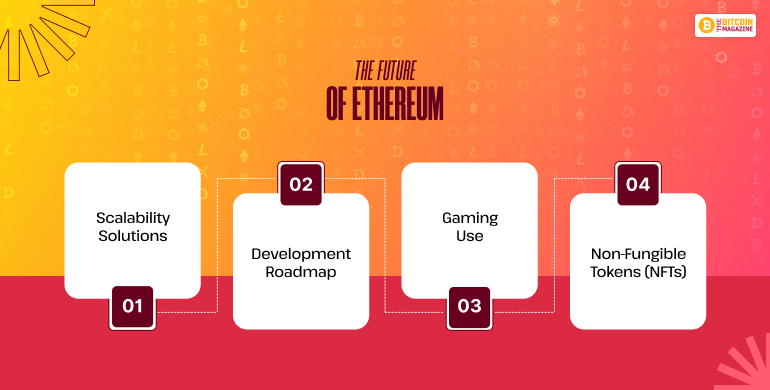
1. Scalability Solutions
- Layer 2 Solutions (L2s): Arbitrum, Optimism, zkSync
- Sharding (Coming): Shattering of the blockchain into shards for processing at a faster speed.
They are necessary in order to support growing adoption without congesting the network.
2. Development Roadmap
There are five stages to Ethereum’s road map:
- The Merge – Completed in 2022
- The Surge – Addition of sharding
- The Verge – Addition of Verkle Trees
- The Purge – Reduction of burden of historical data
- The Splurge – Various performance improvements and bug fixes
3. Gaming Use
Ethereum has revolutionized blockchain gaming:
- Facilitates in-game asset ownership (NFTs).
- Facilitates play-to-earn (P2E) economies.
- Facilitates games like Axie Infinity, Gods Unchained, and The Sandbox.
These games offer users real ownership of virtual property, which can be sold and resold.
4. Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs)
Ethereum pioneered the NFT revolution with its ERC-721 and ERC-1155 standards. NFTs are:
- Digital collectibles (e.g., CryptoPunks, Bored Ape Yacht Club)
- Music, collectibles, and metaverse property
- Ticketing and identity
NFTs are now a multi-billion-dollar industry, and Ethereum is out front.
The Evolution of DAOs
Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs) are another breakthrough enabled by Ethereum.
DAOs are decentralized organizations that self-manage through smart contracts to operate without a central authority.
Examples:
- MakerDAO: Oversees the DAI stablecoin
- Uniswap DAO: Governs the Uniswap protocol
- Friends With Benefits (FWB): A social DAO
DAOs disrupt governance for more transparency and democracy.
What Will Ethereum Be Worth in 2030?

It’s impossible to forecast Ethereum’s price in 2030, but some of the variables that will decide its future price are:
- dApps and DeFi adoption
- Scaling and network upgrades
- Institutional investment
- Global regulatory environment
- Other blockchain competition
Some analysts put ETH at $10,000 to $30,000+ if Ethereum remains at the forefront of smart contracts and scales appropriately.
Why Did Ethereum Fall?

Ethereum price volatility has been brought about by a combination of factors:
- Market Re-balancings: General crypto market trends.
- Fear of Security as a Regulatory Issue: Classification issues.
- Congestion and Gas Fees
- Macro-economic Trends: Interest rates, inflation, geo-politics.
Despite declines, Ethereum has stabilized and increased in the long term.
How Much Is One Ethereum Coin?
As of June 2025, a Ethereum (ETH) is around $3,500, but this varies depending on conditions in the market. To view current prices, you can examine websites such as CoinMarketCap or CoinGecko.
Is Ethereum a Good Buy?
Ethereum has come a long way since its inception in 2015, to become a stable and diversified platform to enable some of our era’s most groundbreaking technology innovations.
From powering DeFi and NFTs, gaming and governance innovation by DAOs, Ethereum is leading the blockchain revolution.
With the growing network and growth through technologies like Layer 2s and sharding, Ethereum’s position as an internet future leader — Web3 — is increasing.
Price targets are questionable, but Ethereum’s developer ecosystem, community standing, and innovation pipeline make it a backbone of the blockchain ecosystem.
No matter if you’re an investor, developer, gamer, or simply interested in the prospects of tech ahead, Ethereum is something you should know about and follow.
Also Read

