An Initial Coin Offering (ICO) is a method of fundraising whereby a blockchain project issues tokens to fund operations and development.
Tokens are normally exchanged for existing cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin (BTC) or Ethereum (ETH) and can offer access to a platform, utility, or future value.
ICOs gained popularity after the sale of Ethereum in 2014 proved to be a success, collecting more than $18 million and accessible to thousands of such initiatives ([Buterin, 2014](https://ethereum.org/en/whitepaper/)).
ICO is an unregulated, decentralized method of traditional fundraising globally with no intermediation of financial institutions.
ICO vs Traditional Fundraising Methods
There is a significant difference when it comes to the traditional method and ICO method of fundraising. So, let’s get to know each of them in detail.
1. Traditional Fundraising
Traditional fundraising methods include:
- Seed/Angel Rounds
- Venture Capital (VC)
- Bank Loans
2. Initial Public Offerings (ICOs)
These are typically exclusive, controlled, and time-consuming. Here in this article you will get to know more about the ins and outs of ICO in this article.([Harvard Business Review, 2021](https://hbr.org/2021/03/the-real-truth-about-vc)).
ICOs: A New Model
| Feature | ICO | Traditional |
| Accessibility | Global | Accredited Investors |
| Speed | Weeks | Months-Years |
| Regulation | Often Unregulated | Heavily Regulated |
| Fees | Low | High legal & Underwriting Fees |
| Equity Control | Retain Control | Give up equity/board seats |
ICOs enable startups to avoid VC control and negotiate with a broader universe of investors ([OECD, 2019] (https://www.oecd.org/finance/initial-coin-offerings-for-sme-financing.htm)).
How an Initial Coin Offering (ICO) Functions

If you are looking into launching an ICO then beforehand you should know how it functions.
1. Select Investment Targets
Explain your project’s:
- Market problem
- Blockchain solution
- Source of revenue
- Token utilization
There must be a valid business case to draw in sponsors.
2. Design Coin Structure
Token Pricing Models:
- Static supply/static price: Fixed tokens with a fixed price.
- Static supply/dynamic price: Price that adjusts as a function of investor demand.
- Dynamic supply/static price: Unlimited token supply, static price
3. Issue Tokens
Employ blockchain standards such as:
- Ethereum (ERC-20)
- Binance Smart Chain (BEP-20)
Tokens are issued through smart contracts ([Ethereum Docs](https://ethereum.org/en/developers/docs/standards/tokens/erc-20/).
4. Publish a Whitepaper
A whitepaper contains:
- Technical overview
- Tokenomics
- Roadmap
- Legal disclaimers
- Team bios
It establishes trust and transparency
5. Run Promotions
Effective channels:
- Reddit, Discord, Telegram
- Airdrops and bounties
- Influencer marketing
Promotions must be made on ethical grounds so that manipulation is not resorted to ([FINRA, 2020](https://www.finra.org/investors/insights/ico-investments)).
6. Pre-Sale Round
Provide institutional or strategic partners with early access to tokens. Usually provides discounted prices (e.g., 20% bonus tokens).
7. ICO Launch
Tokens are sold for a limited time period. Investors place crypto in a wallet, and smart contracts distribute tokens in exchange.
8. Exchange Listing
Following ICO, tokens need to be listed for trading. Exchanges are:
- Centralized
- Decentralized
Listing fosters liquidity and price discovery
Types of Initial Coin Offerings (ICOs)
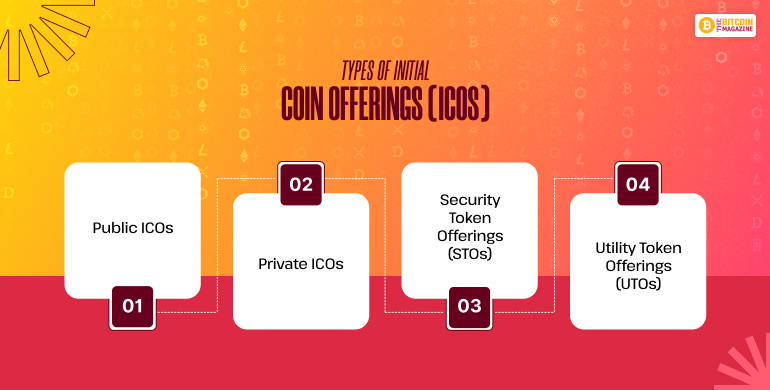
When it comes to Initial Coin Offerings (ICOs), there are several different types of ICOs that you can choose from.
Public ICOs
This is the type of ICO that welcomes investments from various members of the public. It ranges from tiny investors to even large businesses.
The Public ICOs have these major attributes:
- Members who are of the general public, they can easily participate into this type of ICOs.
- The companies and businesses that are launching public ICOs are coupled with marketing this initiative to draw in a more sizable audience.
- Regulation checks like KYC (Know Your Customer) and AML (Anti-Money Laundering) need to be followed.
Private ICOs
When it comes to participate in private ICOs then only a small number of investors can do so, such as institutions, high-net-worth individuals, etc. For this type of ICOs only accredited investors get all the exclusive information.
The major attributes of Private ICOs are:
- The investors must fulfill certain requirements like being an accredited investor and limited participation.
- Since experienced investors are involved in this, they will raise larger sums of money.
- Issuing business may have imposed a minimum amount of investment.
Security Token Offerings (STOs)
When it comes to STOs it is a unique type of ICO for which businesses issue a special coin type, which is categorized as security as per the prevailing regulations.
The major attributes of STOs are:
- The STOs offer a similar type of legal protection as conventional securities.
- These tokens can also be used as a symbolism to ownership in a business or as an asset providing dividends and earnings.
- Investors looking forward to avoiding risk see STOs as more secure and well-regulated than other ICO options.
Utility Token Offerings (UTOs)
With UTOs, the main goal is to create tokens that can grant access to certain goods or services within a particular ecosystem.
The major attributes of UTOs are:
- These tokens are used for platform transactions, such as gaining access to features or making payments for services.
- Unlike security tokens, Utility tokens don’t grant dividends or any ownership rights.
What is Whitepaper?
A whitepaper is the original document that:
- Describes the project vision
- Illustrates the token purpose
- Reveals the technical and legal context
It assists investors in assessing project feasibility.
What Happens to ICO Funds?
- Funds are generally expended as follows:
- Development (40–60%)
- Marketing (10–20%)
- Legal/Compliance (5–15%)
- Team Compensation and Reserves
Best practices are escrow wallets, multisig authorization, and third-party audits to build investor confidence
Who Can Launch an ICO?
Anyone with:
- Something or an idea on the blockchain
- A development team in place
- Legal advice to ensure compliance with regulation
Successful projects have experienced advisors and open business.
Buying into an ICO: Step-by-Step Process
Steps:
1. Load compatible wallet (e.g., MetaMask).
2. Deposit ETH/BTC into wallet.
3. Join via ICO dashboard or smart contract.
4. Get verified and receive tokens later.
Always verify contract addresses not to fall victims of phishing.
ICO Scams
The ICO began decreasing during 2019, partly due to legal grey areas that are there in ICO. With cryptocurrency aggregators you can identify potential scams or other real opportunities. Here are a few warning signs that you should be aware of when launching ICOs.
Warning signs:
- No live product
- Copy-paste content
- Unrealistic returns
- Nameless team
- Transparent paid publicity
Use tools like:
- ICObench, CryptoCompare
- Smart contract audits (CertiK, Hacken)
ICO Hyping
ICOs usually generate a good amount of hype, there are a lot of sites where investors go to discuss new opportunities.
These investors include actors, entertainers, and other celebrities. Along with them you can create hype artificially as well through different sources such as,
Artificial hype is created by:
- Social media bots
- Paid influencers
- Fake endorsements
These practices may lead to pump-and-dump schemes that threaten investor capital.
Initial Coin Offerings: Advantages and Disadvantages
While ICOs have certain several merits concerning both the coin issuers and investors, on the other hand they are associated with a few demerits as well, so let’s check them out.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Democratization of Capital – VCs and international investors both can invest in innovation. | Misuse of Funds – Lack of accountability resulted in rug pulls and exit scams. |
| Free flow of Capital Across Borders – Anyone with a computer and internet access can put money into an ICO. | Legal Uncertainty – Tokens exist primarily in gray regulatory space; some are potential securities. |
| Early Liquidity – Tokens are being sold soon after creation. | Volatility – Tokens usually decline >50% post-ICO because of flipping on speculation. |
| Possibility of High Returns – Ethereum went from $0.30/token to over $4,000 at peak value. | No Legal Remedy – Investors are usually not entitled to receive money back in cases of fraud. |
| Low-Cost Fundraising – Platforms such as EOS raised over $4B within a year. |
ICO vs IPO
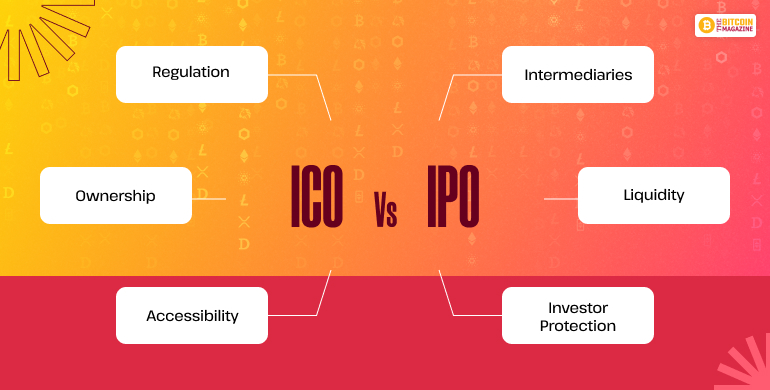
Though the difference is not by a lot but there is significant difference between ICO and IPO, so check out here the different factors where ICO and IPO differ from each other.
| Feature | ICO | IPO |
| Regulation | Light | Strict (SEC, etc.) |
| Ownership | No Equity | Shareholder equity |
| Accessibility | Global | Usually domestic, institution |
| Intermediaries | None | Banks, underwriters |
| Liquidity | Immediate | Generally, lock-up period |
| Investor Protection | Low | High |
ICO Examples
Here are a few examples of Initial Coin Offerings that you should know about.
- Ethereum (2014): Raised $18 million; over 150,000% ROI ([Ethereum Foundation](https://ethereum.org/en/history/#2014-ethereum-ico)).
- EOS (2017–18): $4.1 billion ICO in a year ([Block.one](https://block.one/)).
- Tezos: Raised $232 million; later involved in governance lawsuits ([Tezos Foundation](https://tezos.foundation/)).
- Filecoin: $257 million ICO in 2017 for decentralized storage ([Filecoin Docs](https://filecoin.io/blog/posts/filecoin-token-sale-completed/))
Trade on the Go. Anywhere, Anytime!
ICOs democratized startup funding and injected innovation into global finance. But risk is at the leading edge too, with regulatory risk, fraud, and market volatility.
The future of fundraising can be in hybrid models—Security Token Offerings (STOs), Initial DEX Offerings (IDOs), and more regulated models blending the accessibility of ICOs with legal protections.
Meanwhile, ICOs are an irresponsible and risky way of being at the cutting edge of blockchain technology—wherever, whenever, to whomever.
Also read

